What Fed hates more than inflation... deflation ✌🏼
tion ✌🏼
↓
What does the Fed hate more than inflation? Deflation.
Based on recent data, the U.S. economy is showing signs of deflation.
In this post, I’ll cover:
- Understanding inflation and deflation
- Deflation signs in the U.S. economy
- The Fed’s potential interest rate cut
- The winners of decreasing interest rates
- The opportunities for your online business
What's the deal with inflation and deflation?
Inflation refers to the general increase in prices of goods and services over time, so your money doesn’t go as far.
Deflation is the opposite. You see a general decline in prices, so your money can buy more.
BTW: Disinflation ≠ Deflation.
Prices are still rising in disinflation, just more slowly than they have been.
The Fed hates deflation for 3 reasons.
- Unemployment. As prices drop, company profits decrease, and some companies may cut costs by laying off workers.
- Debt. Interest rates tend to go up in periods of deflation, which makes debt more expensive. Consumers and businesses often decrease spending as a result.
- Economic doom spiral
- Falling prices → Lower production
- Falling production → Lower pay
- Falling pay → Lower demand
- Falling demand → Back to lower prices
The U.S. economy is showing signs of disinflation and deflation
The Fed targets 2% annual inflation for sustainable economic growth.
But the U.S. economy is currently experiencing signs of disinflation and deflation.
The Fed tracks many economic indicators, but these are the 2 to pay attention to.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Producer Price Index (PPI)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures how the prices of things we buy change over time. It tracks typical spending categories like food, housing, and clothing.
By tracking prices of these items, the CPI helps us understand how much more or less we need to spend to buy the same things.
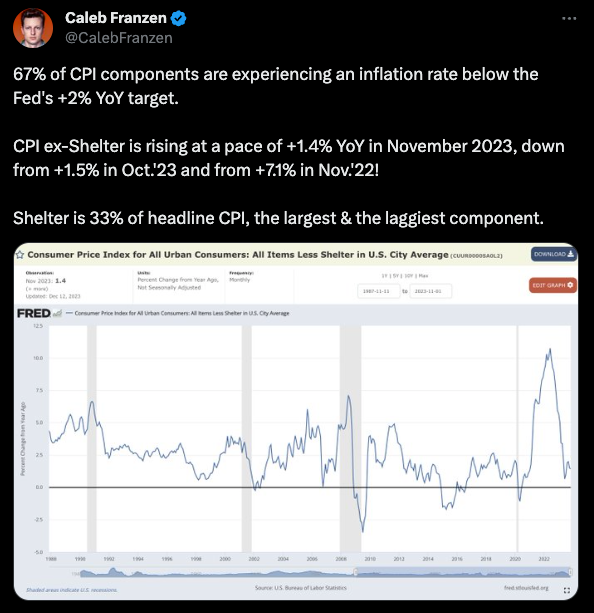
From November's data reports, 67% of CPI components are experiencing an inflation rate below the Fed's 2% target.
Shelter (a.k.a. housing) is a lagging component, so excluding shelter presents a more accurate view of CPI.
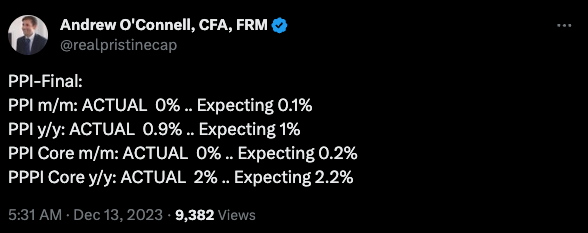
The Producer Price Index (PPI) measures how the prices of goods change at the wholesale level (e.g. manufacturers). This leading indicator helps track inflation before it reaches the consumer.
Recent PPI measurements were LOWER than expected.
The Fed will start cutting interest rates before the 2024 U.S. election.
As more data supports disinflation, the Fed will cut rates for 3 reasons.
- Commercial real estate has $540B debt coming due in 2024, and more in 2025. There is a refinance risk. They will need some relief.
- Banks and financial institutions have bad balance sheets. They hold loans with low interest rates. The prices for those loans took a nose dive. With current accounting standards, they don’t have to recognize losses until they sell the loans.
- Government debt will be unsustainable. The government is borrowing more money to pay debt. At current rates, the government will spend more money on interest than defense in four years.
On top of that, 2024 is U.S. election year.
The economy remains top of mind for American voters.
Both Democrat and Republican candidates need to pump the economy.
So the Fed will be under a lot of pressure to cut interest rates leading up to the election.
The winners of decreasing interest rates are...
Lower interest rates make borrowing and spending money cheaper.
Let’s evaluate by:
- Industry
- Market Capitalization (e.g. company size)
- US vs Rest of World
Industry
Lower interest rates encourages consumer spending, especially for non-essential purchases.
Industries that may benefit from lower interest rates:
- Real estate and home improvement
- Financials (e.g. banks, lenders, fintech)
- Consumer discretionary (e.g. cars, fashion, appliances, restaurants)
Market Capitalization
Market capitalization, often referred to as “market cap,” is a measure of a company’s size and value in the stock market.
It is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the total number of outstanding shares. The investment community uses market cap to determine a company’s size instead of sales or total asset figures.
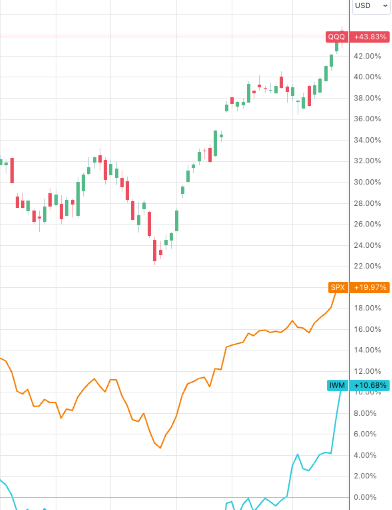
Small caps ($IWM), companies with $25M-$2B market caps, has to play catch-up with its bigger sibling, SP500 ($SPX), and the red-hot tech sector ($QQQ).
US vs Rest of World
In 2023, international markets ($ACWX) lagged behind the US market ($VTI).
The US dollar may have peaked for the cycle with the Fed signaling rate cuts in 2024. A weaker US dollar has historically been associated with strong international equity performance because a weaker dollar means more purchasing power for local consumers around the world. Emerging market economics with dollar-denominated debt typically benefit most from a weaker dollar.
In 2022, emerging market stocks - as measured by MSCI Emerging Markets Index - traded close to price-to-book and price-to-earnings levels seen during the 2008-2009 Global Financial Crisis. Despite a strong start in 2023, international stocks are still trading at a significant discount to U.S. equities.
What does this mean for your online business?
Here are some scenarios to consider:
You want to raise venture capital for your business
When rates go lower, there will be a higher appetite for venture investing, but this won’t happen overnight.
Venture investors continue to pursue deals with low valuations for maximum upside, so the majority of funds will remain selective through first half of 2024.
Your company is likely to secure funding if it exhibits these 3 traits:
- Strong team who have previously worked together at high-growth startups or prior exits
- Working prototype or product with strong user adoption and feedback
- Accelerating traction in revenue
If you don’t have these 3 checkboxes, it’s best to understand how much of a gap you have and do whatever it takes to close the gap.
Fundraising markets will likely stabilize and recover 2024 post-US election, as LPs (the investors investing in venture funds) will recycle their returns into new funds.
You sell online services
When rates go lower, it will be easier for businesses to access working capital for operations. They will be more likely to fund new projects that could lead to future business growth.
Since 2024 is an election year, online advertising will be more expensive. Existing businesses will allocate more resources to building their organic SEO traffic to their websites and social media channels. Businesses, regardless of size and industry, will need to integrate organic content as part of their integrated marketing campaigns.
There will be opportunities for services businesses to serve these businesses given the number of social media platforms, mediums (video, text), and languages.
At the same time, there will be more competition. It will be critical to narrow your target customer profile to differentiate your business.
You sell digital products
Businesses are continuing to evaluate their software stack for their operations across all functions. While technologies such as AI can boost productivity and create new job opportunities, these innovations can automate certain tasks leading to potential job displacement.
Demand for educational products will increase, as more people seek to learn new skills or augment existing skills. Technology makes the creation and distribution of these products more accessible, so it is possible to build revenue-generating businesses serving smaller audience niches.
In summary, the Fed’s aversion to deflation is rooted in its potential to disrupt consumer behavior, increase the burden of debt, dampen investment, and limit the effectiveness of monetary policy. These factors make deflation a significant concern for the Fed in its efforts to maintain economic stability and growth.